- Home
- Algorithms
- Unit Convert
Unit Convert
Welcome to my unit convert tools and guide, your go-to resource for simplifying the complex world of measurement conversions. Whether you're a student, professional, or simply curious, this guide offers clear explanations and easy-to-follow steps for converting between various units of length, weight, volume, temperature, and more.
Of course, every explanation is followed by an example implementation in C, as well as a web tool. Unlock the ability to seamlessly transition from kilometers to miles, pounds to kilograms, or Celsius to Fahrenheit, and countless other conversions. With my user-friendly format and practical examples, mastering unit conversions has never been more accessible. Enhance your understanding and save time with my indispensable unit conversion companion.
- Universal Unit Convertor - combines all of the other converters in one place
- Length
(Metric -> Imperial)
* Kilometers to Miles
* Meters to Feet
* Centimeters to Inches
(Imperial -> Metric)
* Miles to Kilometers
* Feet to Meters
* Inches to Centimeters - Weight
(Metric -> Imperial)
* Tons to Pounds
* Kilograms to Pounds
* Grams to Ounces
(Imperial -> Metric)
* Pounds to Tons
* Pounds to Kilograms
* Ounces to Grams - Volume
(Metric -> Imperial)
* Liters to Gallons
* Milliliter to Ounces
(Imperial -> Metric)
* Gallons to Liters
* Ounces to Milliliters - Temperature
Celsius to Fahrenheit
Fahrenheit to Celsius
Universal Unit Converter
Here's an example of an HTML form with JavaScript that handles unit
conversion between metric and imperial measurement systems based on the
user's selection. After you change the value for the first unit, the second unit will be automatically filled.
This form allows users to select different measurement units from a dropdown list and then enter a value to convert. The available output units are dynamically updated based on the selected input unit. When the "Convert" button is clicked, the result is displayed.
This is the entire example in C, combining all of the conversions described below. Each of them is explained in more details in the relevant section.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 | #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> void updateOutputUnitOptions(const char *inputUnit, char outputUnits[][3], int *numOutputUnits) { if (strcmp(inputUnit, "km") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "mi"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "m") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "ft"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "cm") == 0 || strcmp(inputUnit, "mm") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "in"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "mi") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "km"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "ft") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "m"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "in") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 2; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "cm"); strcpy(outputUnits[1], "mm"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "ton") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "lb"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "kg") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "lb"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "g") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "oz"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "lb") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 2; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "ton"); strcpy(outputUnits[1], "kg"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "oz") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "g"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "L") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "gal"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "ml") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "floz"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "gal") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "L"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "floz") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "ml"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "C") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "F"); } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "F") == 0) { *numOutputUnits = 1; strcpy(outputUnits[0], "C"); } else { *numOutputUnits = 0; } } double convert(const char *inputUnit, const char *outputUnit, double inputValue) { double result; if (strcmp(inputUnit, outputUnit) == 0) { result = inputValue; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "km") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "mi") == 0) { result = inputValue * 0.621371; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "m") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "ft") == 0) { result = inputValue * 3.28084; } else if ((strcmp(inputUnit, "cm") == 0 || strcmp(inputUnit, "mm") == 0) && strcmp(outputUnit, "in") == 0) { result = inputValue * 0.393701; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "mi") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "km") == 0) { result = inputValue * 1.60934; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "ft") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "m") == 0) { result = inputValue * 0.3048; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "in") == 0 && (strcmp(outputUnit, "cm") == 0 || strcmp(outputUnit, "mm") == 0)) { result = inputValue * 2.54; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "ton") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "lb") == 0) { result = inputValue * 2204.62; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "kg") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "lb") == 0) { result = inputValue * 2.20462; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "g") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "oz") == 0) { result = inputValue * 0.03527396; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "lb") == 0 && (strcmp(outputUnit, "ton") == 0 || strcmp(outputUnit, "kg") == 0)) { result = inputValue * 0.453592; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "oz") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "g") == 0) { result = inputValue * 28.3495; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "L") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "gal") == 0) { result = inputValue * 0.264172; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "ml") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "floz") == 0) { result = inputValue * 0.033814; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "gal") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "L") == 0) { result = inputValue * 3.78541; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "floz") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "ml") == 0) { result = inputValue * 29.5735; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "C") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "F") == 0) { result = (inputValue * 9 / 5) + 32; } else if (strcmp(inputUnit, "F") == 0 && strcmp(outputUnit, "C") == 0) { result = (inputValue - 32) * 5 / 9; } else { result = 0; // Invalid conversion } return result; } int main() { char inputUnit[3], outputUnit[3]; double inputValue, result; char outputUnits[2][3]; int numOutputUnits; printf("Unit Converter\n"); // Prompt user for input printf("Enter input unit: "); scanf("%s", inputUnit); updateOutputUnitOptions(inputUnit, outputUnits, &numOutputUnits); if (numOutputUnits == 0) { printf("Invalid input unit.\n"); return 1; } printf("Select output unit:\n"); for (int i = 0; i < numOutputUnits; i++) { printf("%d. %s\n", i + 1, outputUnits[i]); } printf("Choice: "); int choice; scanf("%d", &choice); if (choice < 1 || choice > numOutputUnits) { printf("Invalid choice.\n"); return 1; } strcpy(outputUnit, outputUnits[choice - 1]); printf("Enter input value: "); scanf("%lf", &inputValue); result = convert(inputUnit, outputUnit, inputValue); printf("%.2f %s is equal to %.2f %s\n", inputValue, inputUnit, result, outputUnit); return 0; } |
Length Unit Convert: Metric to Imperial
Kilometers to Miles
Converting kilometers to miles is a straightforward process using a simple conversion factor. One kilometer is approximately equal to 0.621371 miles.
To convert kilometers to miles, multiply the distance in kilometers by the conversion factor 0.621371. For example, if you have 10 kilometers to convert, you would calculate: 10 km × 0.621371 ≈ 6.21371 miles. This simple formula allows you to quickly and easily convert distances from the metric system (kilometers) to the imperial system (miles).
Here is a simple example in C which does the unit convert:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | #include <stdio.h> int main() { double kilometers, miles, conversionFactor; // Prompt the user to enter distance in kilometers printf("Enter distance in kilometers: "); scanf("%lf", &kilometers); // Conversion factor: 1 kilometer = 0.621371 miles conversionFactor = 0.621371; // Perform the conversion miles = kilometers * conversionFactor; // Display the result printf("%.2f kilometers is equal to %.2f miles.\n", kilometers, miles); return 0; } |
Meters to Feet
TODO: output = feet+inches
Converting meters to feet is accomplished by multiplying the distance in meters by the conversion factor 3.28084.
For instance, if given a length of 10 meters, the conversion is calculated as follows: 10 m × 3.28084 ≈ 32.8084 ft. This straightforward formula allows a seamless transition between the metric (meters) and imperial (feet) systems, and it's frequently utilized in engineering, construction, and everyday measurements.
The unit convert done with a C function:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | #include <stdio.h> int main() { double meters, feet, conversionFactor; // Prompt the user to enter length in meters printf("Enter length in meters: "); scanf("%lf", &meters); // Conversion factor: 1 meter = 3.28084 feet conversionFactor = 3.28084; // Perform the conversion feet = meters * conversionFactor; // Display the result printf("%.2f meters is equal to %.2f feet.\n", meters, feet); return 0; } |
Centimeters to Inches
Each centimeter is roughly equivalent to 0.393701 inches
To convert, you take the number of centimeters you have and multiply it by this conversion factor. For instance, if you have 20 centimeters and want to know how many inches that is, you would do: 20 cm × 0.393701 ≈ 7.87402 inches.
Example implementation in C:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | #include <stdio.h> int main() { double centimeters, inches, conversionFactor; // Prompt the user to enter length in centimeters printf("Enter length in centimeters: "); scanf("%lf", ¢imeters); // Conversion factor: 1 centimeter = 0.393701 inches conversionFactor = 0.393701; // Perform the conversion inches = centimeters * conversionFactor; // Display the result printf("%.2f centimeters is equal to %.2f inches.\n", centimeters, inches); return 0; } |
And the output of the program looks like this:
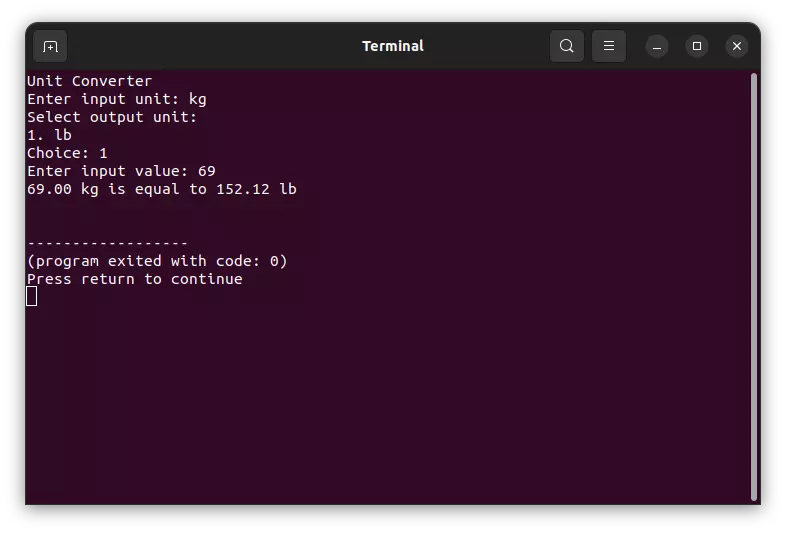
Length Unit Convert: Imperial to Metric
Miles to Kilometers
One mile is approximately equal to 1.60934 kilometers.
To perform the conversion, just multiply the number of miles by this conversion factor. For instance, if you have 10 miles, the calculation would be: 10 miles × 1.60934 ≈ 16.0934 kilometers.
In this C example, the user is prompted to enter a distance in miles. The program then does the unit convert and displays the result.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | #include <stdio.h> int main() { double miles, kilometers, conversionFactor; // Prompt the user to enter distance in miles printf("Enter distance in miles: "); scanf("%lf", &miles); // Conversion factor: 1 mile = 1.60934 kilometers conversionFactor = 1.60934; // Perform the conversion kilometers = miles * conversionFactor; // Display the result printf("%.2f miles is equal to %.2f kilometers.\n", miles, kilometers); return 0; } |
Feet to Meters
One foot is equal to approximately 0.3048 meters. This will be our unit conversion factor.
To perform the conversion, you multiply the number of feet by this conversion factor.
Done in C, this will look like this:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | #include <stdio.h> int main() { double feet, meters, conversionFactor; // Prompt the user to enter length in feet printf("Enter length in feet: "); scanf("%lf", &feet); // Conversion factor: 1 foot = 0.3048 meters conversionFactor = 0.3048; // Perform the conversion meters = feet * conversionFactor; // Display the result printf("%.2f feet is equal to %.2f meters.\n", feet, meters); return 0; } |
Inches to Centimeters
One inch is equal to exactly 2.54 centimeters.
To convert inches to centimeters, simply multiply the number of inches by this number.
Here is a short C program which does just that.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | #include <stdio.h> int main() { double inches, centimeters, conversionFactor; // Prompt the user to enter length in inches printf("Enter length in inches: "); scanf("%lf", &inches); // Conversion factor: 1 inch = 2.54 centimeters conversionFactor = 2.54; // Perform the conversion centimeters = inches * conversionFactor; // Display the result printf("%.2f inches is equal to %.2f centimeters.\n", inches, centimeters); return 0; } |
Weight (Metric -> Imperial)
Tons to Pounds
A metric ton, often denoted as "t" or "MT," is a unit of mass or weight in the metric system. It is equivalent to 1,000 kilograms (kg) or approximately 2,204.62 pounds (lbs).
If your are interested of how to write your own program which does the unit convert, here is how I would do it in C:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | #include <stdio.h> int main() { double tons, pounds, conversionFactor; // Prompt the user to enter weight in metric tons printf("Enter weight in metric tons: "); scanf("%lf", &tons); // Conversion factor: 1 ton = 2000 pounds conversionFactor = 2204.62; // Perform the conversion pounds = tons * conversionFactor; // Display the result printf("%.2f metric tons is equal to %.2f pounds.\n", tons, pounds); return 0; } |
Kilograms to Pounds
One kilogram is equal to approximately 2.20462 pounds.
For example, if you have 5 kilograms, you would calculate: 5 kg × 2.20462 = 11.0231 pounds.
In this example, the user is prompted to enter a weight in kilograms.
The program then performs the unit convert with the entered
kilograms to pounds and displays the result.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | #include <stdio.h> int main() { double kilograms, pounds, conversionFactor; // Prompt the user to enter weight in kilograms printf("Enter weight in kilograms: "); scanf("%lf", &kilograms); // Conversion factor: 1 kilogram = 2.20462 pounds conversionFactor = 2.20462; // Perform the conversion pounds = kilograms * conversionFactor; // Display the result printf("%.2f kilograms is equal to %.2f pounds.\n", kilograms, pounds); return 0; } |
Grams to Ounces
A gram and an ounce are both units of weight or mass used to measure the amount of matter in an object, but they belong to different measurement systems. The gram is a unit in the metric system, while the ounce is a unit in the imperial system.
1 gram is approximately equal to 0.03527396 ounces.
These units are often used in cooking, scientific research and international trade. Converting between them is done easily with the form above.
Here's a C routine to explain how it is done:
1 2 3 4 5 | double gramsToOunces(double grams) { // Conversion factor: 1 gram = 0.03527396 ounces double conversionFactor = 0.03527396; return grams * conversionFactor; } |
Weight (Imperial -> Metric)
Pounds to Tons
1 pound is equal to approximately 0.0005 tons.
However, there are two main types of tons: the short ton (often used in the United States) and the metric ton (also known as a tonne). In the imperial system, 1 short ton is equal to 2,000 pounds. In the metric system, 1 metric ton (tonne) is equal to 1,000 kilograms (approximately 2,204.62 pounds).
The form above and the C routine below use the metric ton.
double poundsToMetricTons(double pounds) { // Conversion factor: 1 metric ton = 2204.62 pounds double conversionFactor = 2204.62; return pounds / conversionFactor; }
Pounds to Kilograms
1 pound is approximately equal to 0.453592 kilograms.
Pounds are often used in countries that use the imperial system, like the United States and the United Kingdom, for everyday weight measurements such as people's weight, grocery items, and body measurements. Kilograms, on the other hand, are widely used around the world as the standard unit for scientific measurements, international trade, and more precise weight measurements in fields such as physics, engineering, and medicine.
The unit convert from pounds to kilogram can easily be implemented into a C function:
double poundsToKilograms(double pounds) { // Conversion factor: 1 pound = 0.453592 kilograms return pounds * 0.453592; }
Ounces to Grams
Ounces are commonly used in the imperial system, particularly in the US
and UK, for small weight measurements like food and liquids.
Grams, part of the metric system, are widely used internationally and in science. 1 ounce is approximately equal to 28.3495 grams.
Implementation in C:
double ouncesToGrams(double ounces) { // Conversion factor: 1 ounce = 28.3495 grams return ounces * 28.3495; }
Volume (Metric -> Imperial)
Liters to Gallons
Liters are utilized internationally and are commonly used for measuring liquids in various applications, including scientific research, industries, and consumer products. On the other hand, gallons are primarily used in the United States, existing in both imperial and US customary forms.
1 liter is approximately equal to:
- 0.26417 US gallons
- 0.21997 imperial gallons
The unit converter above uses US gallons.
Here's how to do it in C:
double litersToUSGallons(double liters) { // Conversion factor: 1 liter = 0.26417 US gallons return liters * 0.26417; }
Milliliter to Ounces
There are fluid ounces (fl oz) and dry ounces, each with different conversion ratios. The ratio between milliliters and US fluid ounces is approximately 1 ml to 0.033814 fl oz
In this example, the millilitersToUSFluidOunces function takes a volume in milliliters as input and returns the equivalent volume in US fluid ounces by multiplying the volume by the conversion factor.
double millilitersToUSFluidOunces(double milliliters) { // Conversion factor: 1 milliliter = 0.033814 US fluid ounces return milliliters * 0.033814; }
Volume (Imperial -> Metric)
Gallons to Liters
1 US gallon is approximately equal to 3.78541 liters.
1 imperial gallon is approximately equal to 4.54609 liters.
These ratios illustrate the differences in volume between gallons used in the imperial and US customary systems and liters, which are part of the metric system.
Converting between these units of volume measurement requires using these specific conversion factors. In the unit converter above we are using a US gallon.
Here's the C example:
double gallonsToLiters(double gallons) { // Conversion factor: 1 gallon = 3.78541 liters return gallons * 3.78541; }
Ounces to Milliliters
Ounces:
- Ounces have two main types: fluid ounces (fl oz) and dry ounces.
- 1 US fluid ounce (fl oz) is approximately 29.5735 milliliters.
- Ounces are commonly used in the United States for cooking, beverage measurements, and product labeling.
- The precise conversion factor depends on whether it's a fluid ounce or dry ounce.
Milliliters:
- Milliliters are used globally as a standard unit of volume in the metric system.
- 1 milliliter (ml) is equal to 0.033814 US fluid ounces.
- Milliliters offer a consistent and easily convertible approach, commonly used in scientific research, pharmaceuticals, and cooking.
double ouncesToMilliliters(double ounces) { // Conversion factor: 1 ounce = 29.5735 milliliters return ounces * 29.5735; }
Temperature
Celsius to Fahrenheit
Celsius and Fahrenheit are two temperature scales used to measure temperature, but they have different reference points and increments.
To do the unit convert from Celsius to Fahrenheit, use the formula: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Celsius:
- Celsius (°C) is a metric temperature scale widely used globally, especially in scientific and everyday contexts.
- The freezing point of water is 0°C, and the boiling point is 100°C under standard atmospheric pressure.
- Positive values represent above-freezing temperatures, while negative values indicate below-freezing temperatures.
double celsiusToFahrenheit(double celsius) { return (celsius * 9 / 5) + 32; }
Fahrenheit to Celsius
We unit convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius with the formula: °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
double fahrenheitToCelsius(double fahrenheit) { return (fahrenheit - 32) * 5 / 9; }
- Home
- Algorithms
- Unit Convert
 Manage the football team of your city and make them champions!
Manage the football team of your city and make them champions!
 Manage the football team of your city and make them champions!
Manage the football team of your city and make them champions!
 Manage the football team of your city and make them champions!
Manage the football team of your city and make them champions!